Top Ten Patient Safety Issues 2018
 Patient safety issues for providers to prioritize in 2018, presented below in no particular order, are the top 10 patient safety issues reported in the past year.
Patient safety issues for providers to prioritize in 2018, presented below in no particular order, are the top 10 patient safety issues reported in the past year.
Table of Contents
1.) Disparate electronic health records (EHRs)
This contributes to poor interoperability, putting patients at risk for events such as medication mixing. This can negatively affect patient care.
A lack of interoperability may mean providers are not getting the whole picture when it comes to their patients’ conditions. It also makes effective patient care harder in times of crisis or during natural disasters.
2.) Hand hygiene
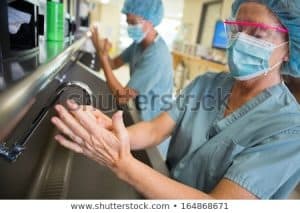
This remains as a top safety concern, as noncompliance was linked with several infections and even death.
While it may seem difficult to control the actions of an entire health system staff, interventions such as signage, smart notifications, and education can significantly increase compliance and save lives.
3.) Nurse-patient ratios
Inadequate staffing at healthcare facilities can greatly affect patient care.
One study published in the International Journal of Nursing Studies demonstrated that for every additional patient on a nurse’s caseload, mortality rates increased by seven percent.
4.) Shortages of drugs and medical supplies
The supply chain is responsible for a surprising number of adjustments to patient care. In May, many hospitals were forced to delay major operations and chemotherapy treatments due to a nationwide shortage of sodium bicarbonate solution.
5.) Quality reporting
When paperwork demands more time than patient care, there’s cause for reexamination.
Hospital systems can improve the patient experience and prevent the next safety threat on the list.
CMS plans to simplify the measures hospitals and physicians must report on, zeroing in on the most important measures to improve care quality and patient outcomes.
6.) Physician burnout
Physician shortage has been an increasing problem. This impacts the majority of physicians, with a nearly 20 percent increase in those reporting symptoms in the last five years.
The healthcare executives argued addressing burnout should be a major priority for all healthcare leaders, as it can threaten patient safety, quality of care and increase healthcare costs.
7.) Resurgent diseases
Scarlet fever and measles are once again threatening patient safety.
Misinformation about vaccines led to an unfortunate drop in immunization rates, posing a direct threat to both public and patient safety and must be accounted for.
 8.) Mergers and acquisitions
8.) Mergers and acquisitions
Health and hospital networks can bring many positive changes for everyone involved, but they also pose a safety risk.
Research shows patients living in competitive healthcare markets exhibit better health outcomes and lower mortality rates than those who live in areas with less healthcare competition.
9.) Antibiotic resistance
It posed a world health concern for many years.
This issue is highly complex in terms of both social and biological science and the international community must continue to work toward a solution.
Infection control leaders can look to organizations for tools to improve antibiotic stewardship and resistance.
10.) The opioid epidemic
 It remains critical that healthcare leaders stay diligent about promoting more responsible medical use of opioids.
It remains critical that healthcare leaders stay diligent about promoting more responsible medical use of opioids.
Three physician leaders argued hospitals should be penalized for opioid addiction if the condition develops as a result of hospital-based care that could have been prevented by adhering to evidence-based practices.
To receive the latest hospital and health system news, visit us weekly for updates.
